Introduction
Hello friends, my name is Himanshu Sen and with the help of our website sarkarijobhere.com, I will tell you all the information related to new government jobs, private jobs, online jobs, work-from-home jobs, government schemes and news related to all these. Please read this article completely so that you can get complete information.
Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) is a significant component of the Indian taxation system. It is a mechanism through which the government collects taxes at the source of income generation. As a taxpayer, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of TDS to ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid any unnecessary penalties. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of TDS, its applicability, how it works, and its implications on taxpayers and deductors alike.
Table of Contents
- What is TDS?
- Why is TDS Deducted?
- Applicability of TDS
- TDS on Salary
- TDS on Interest Income
- TDS on Rent
- TDS on Professional Fees
- TDS on Contractor Payments
- TDS on Commission
- How TDS Works
- TDS Rates and Thresholds
- TDS Certificate – Form 16 and Form 16A
- How to Calculate TDS
- TDS Return Filing
- TDS Refund Process
- Consequences of Non-Compliance
- TDS and Advance Tax
- TDS vs. TCS (Tax Collected at Source)
- Common TDS Errors and How to Avoid Them
- TDS in Digital Transactions
- Conclusion
1. What is TDS?
TDS, or Tax Deducted at Source, is a system that requires individuals or entities to deduct a certain percentage of tax from the payment made to another person. The deducted tax amount is then deposited with the government on behalf of the recipient.
2. Why is TDS Deducted?
TDS serves two primary purposes:
- Regular Source of Revenue for the Government: TDS ensures a steady inflow of revenue to the government throughout the financial year, helping in funding various public welfare initiatives and developmental projects.
- Preventing Tax Evasion: TDS acts as a check against tax evasion, as tax is deducted at the time of payment itself, leaving little scope for the taxpayer to evade tax.
3. Applicability of TDS
TDS is applicable to various types of payments. Let’s explore some common scenarios:
– TDS on Salary
Employers deduct TDS on the salary paid to employees based on their income tax slab rates.
– TDS on Interest Income
Financial institutions deduct TDS on interest income earned from fixed deposits, recurring deposits, or other interest-bearing instruments.
– TDS on Rent
Individuals and entities paying rent above a specified threshold must deduct TDS before paying the landlord.
– TDS on Professional Fees
Payments made to professionals such as doctors, lawyers, or consultants are subject to TDS.
– TDS on Contractor Payments
Payments made to contractors and sub-contractors are liable for TDS deduction.
– TDS on Commission
TDS is deducted from the commission paid to agents and brokers.
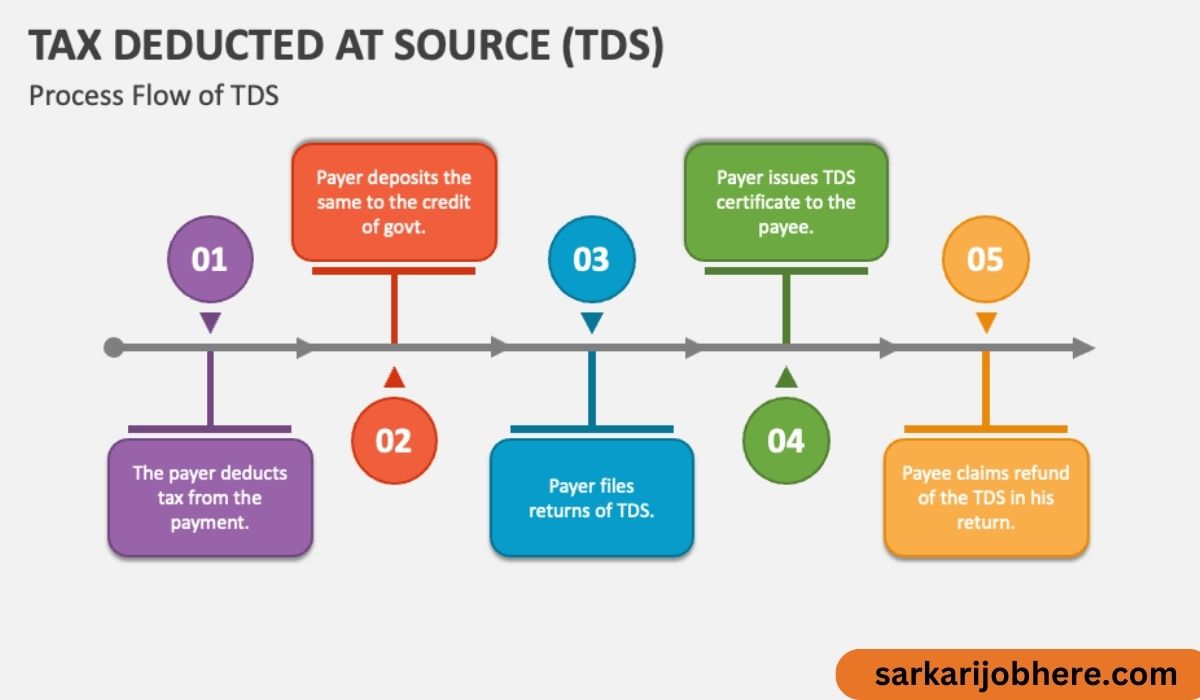
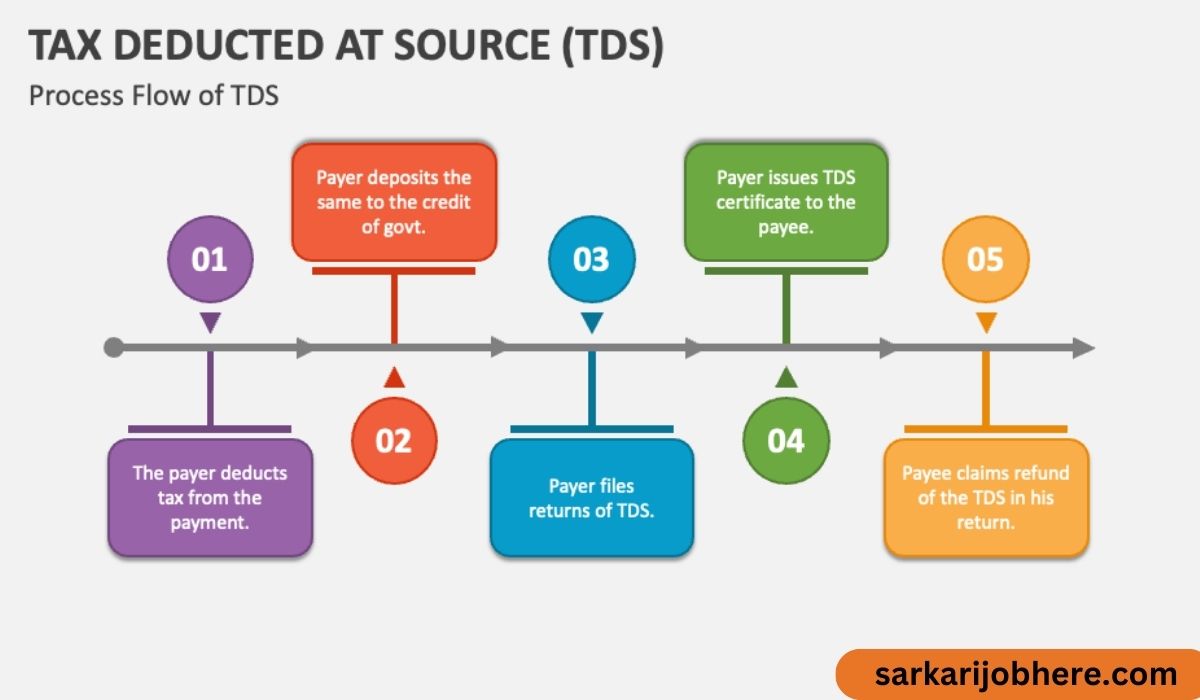
4. How TDS Works
When a payment is made to a payee, the deductor (person making the payment) deducts a specific percentage of the payment as TDS and deposits it with the government. The deductor then issues a TDS certificate to the payee as proof of tax deduction.
5. TDS Rates and Thresholds
TDS rates vary based on the nature of payment and the payee’s income. Different sections of the Income Tax Act prescribe different rates for various payments.
6. TDS Certificate – Form 16 and Form 16A
Form 16 is a TDS certificate issued by employers, while other deductors issue Form 16A. These certificates provide details of the TDS deducted and other relevant information.
7. How to Calculate TDS
Calculating TDS involves considering the applicable TDS rate and the amount paid to the payee.
8. TDS Return Filing
Deductors are required to file TDS returns periodically, providing details of TDS deducted and deposited.
9. TDS Refund Process
If excess TDS has been deducted, the payee can claim a refund while filing their income tax return.
10. Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to deduct TDS or depositing it late can attract penalties and interest.
11. TDS and Advance Tax
Understanding the difference between TDS and advance tax is crucial for taxpayers.
12. TDS vs. TCS (Tax Collected at Source)
TDS and TCS are similar concepts, but they apply to different types of transactions.
13. Common TDS Errors and How to Avoid Them
Avoiding common TDS errors helps in smooth tax compliance.
14. TDS in Digital Transactions
The applicability of TDS in the digital economy and its challenges.
15. Conclusion
In conclusion, TDS plays a pivotal role in the Indian tax system. It ensures a regular source of revenue for the government and discourages tax evasion. As taxpayers, understanding TDS and its implications is crucial for smooth compliance with tax laws.
FAQs
1. What happens if TDS is not deducted?
If TDS is not deducted or not deposited on time, the deductor may attract penalties and interest under the Income Tax Act.
2. Can I claim a refund for the excess TDS deducted?
Yes, if excess TDS is deducted, you can claim a refund while filing your income tax return.
3. Is TDS applicable to all types of payments?
No, TDS is applicable only to specific payments as mentioned under the Income Tax Act.
4. Can I avoid a TDS deduction on my salary?
No, TDS on salary is mandatory, and employers are required to deduct it based on your income tax slab rates.
5. What is the due date for filing TDS returns?
TDS returns must be filed quarterly, and the Income Tax Department specifies the due dates.